|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A discontinuity is: |
a. always a defect |
b. always a reject |
c. always acceptable |
d. rejectable if it exceeds code limits |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
Of the following, which is commonly caused by the presence of hydrogen in a crack susceptible microstructure subjected to applied stress? |
a. lamellar tearing |
b. delamination |
c. porosity |
d. delayed cracking |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
Porosity, occurring in the form of large cylindrical pores is called: |
a. clustered porosity |
b. linear scattered porosity |
c. uniformly scattered porosity |
d. elongated porosity |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
Which of the following discontinuities is least likely to be detected visually? |
a. toe crack |
b. undercut |
c. lamellar tear |
d. overlap |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
Underbead cracks can result from which of the following welding practices? |
a. use of wet electrodes |
b. welding on contaminated steels |
c. welding over paint |
d. all of the above |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
The weld discontinuity that results from improper termination of the welding arc is referred to as: |
a. undercut |
b. overlap |
c. crater crack |
d. incomplete fusion |
e. all of the above |
|
|
|
All but which of the following processes may result in the presence of slag inclusions in the completed weld? |
a. SMAW |
b. PAW |
c. FCAW |
d. SAW |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
That discontinuity that results from the entrapment of gas within the weld cross section is referred to as: |
a. crack |
b. slag inclusion |
c. incomplete fusion |
d. porosity |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
What base metal discontinuity, located at the weld toe, is caused by the welder traveling too rapidly? |
a. underfill |
b. undercut |
c. incomplete fusion |
d. overlap |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
What weld discontinuity results when the welder travels too slowly, which causes excess weld metal to pour out of the joint and lay on the base metal surface without fusing? |
a. undercut |
b. underfill |
c. overlap |
d. incomplete fusion |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
What weld metal discontinuity results when the welder fails to completely fill the weld groove? |
a. underfill |
b. undercut |
c. overlap |
d. incomplete fusion |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
Excessive weld metal buildup on a groove weld is referred to as: |
a. excess convexity |
b. excess weld reinforcement |
c. overfill |
d. all of the above |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
The weld discontinuity that results from the initiation of the welding arc outside the weld joint is referred to as: |
a. incomplete fusion |
b. undercut |
c. overlap |
d. scratch start |
e. arc strike |
|
|
|
Of the following, which weld discontinuity shows up as a light region on a radiograph? |
a. porosity |
b. incomplete joint penetration |
c. a and b above |
d. tungsten inclusion |
e. none of the above |
|
|
|
What base metal discontinuity results from improper steelmaking practice and is associated with the rolled surface? |
a. lamination |
b. delamination |
c. seam |
d. crack |
e. none of the above |
|
|
16- 20 |
|
||||||
|
|
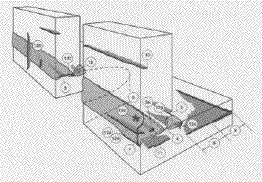
What discontinuity is shown by #12b? |
a. longitudinal crack |
b. transverse crack |
c. face crack |
d. toe crack |
e. root crack |
|
|
|
What discontinuity is shown by #11? |
a. lamination |
b. base metal crack |
c. lamellar tear |
d. seam |
e. lap |
|
|
|
What discontinuity is shown by #12g? |
a. toe crack |
b. incomplete fusion |
c. root crack |
d. lamellar tear |
e. underbead crack |
|
|
|
What discontinuity is shown by #5? |
a. undercut |
b. underfill |
c. overlap |
d. incomplete fusion |
e. toe crack |
|
|
|
What discontinuity is shown by #10? |
a. lamination |
b. seam |
c. delamination |
d. base metal crack |
e. incomplete fusion |
|